管道开发工具
Jenkins Pipeline includes built-in documentation and the Snippet Generator which are key resources when developing Pipelines. They provide detailed help and information that is customized to the currently installed version of Jenkins and related plugins. In this section, we’ll discuss other tools and resources that may help with development of Jenkins Pipelines.
Blue Ocean编辑器
Blue Ocean Pipeline 编辑器提供一个所见即所得的 provides a WYSIWYG way to create Declarative Pipelines. The editor offers a structural view of all the stages, parallel branches, and steps in a Pipeline. The editor validates Pipeline changes as they are made, eliminating many errors before they are even committed. Behind the scenes it still generates Declarative Pipeline code.
Command-line Pipeline Linter
Jenkins can validate, or "lint", a Declarative Pipeline from the command line before actually running it. This can be done using a Jenkins CLI command or by making an HTTP POST request with appropriate parameters. We recommended using the SSH interface to run the linter. See the Jenkins CLI documentation for details on how to properly configure Jenkins for secure command-line access.
Linting via the CLI with SSH
# ssh (Jenkins CLI)
# JENKINS_SSHD_PORT=[sshd port on master]
# JENKINS_HOSTNAME=[Jenkins master hostname]
ssh -p $JENKINS_SSHD_PORT $JENKINS_HOSTNAME declarative-linter
<
Jenkinsfile
Linting via HTTP POST using
curl
# curl (REST API)
# Assuming "anonymous read access" has been enabled on your Jenkins instance.
# JENKINS_URL=[root URL of Jenkins master]
# JENKINS_CRUMB is needed if your Jenkins master has CRSF protection enabled as it should
JENKINS_CRUMB=`curl "$JENKINS_URL/crumbIssuer/api/xml?xpath=concat(//crumbRequestField,\":\",//crumb)"`
curl -X POST -H $JENKINS_CRUMB -F "jenkinsfile=
<
Jenkinsfile" $JENKINS_URL/pipeline-model-converter/validate
Examples
Below are two examples of the Pipeline Linter in action. This first example shows the output of the linter when it is passed an invalid Jenkinsfile, one that is missing part of the agent declaration.
Jenkinsfile
pipeline {
agent
stages {
stage ('Initialize') {
steps {
echo 'Placeholder.'
}
}
}
}
Linter output for invalid Jenkinsfile
# pass a Jenkinsfile that does not contain an "agent" section
ssh -p 8675 localhost declarative-linter
<
./Jenkinsfile
Errors encountered validating Jenkinsfile:
WorkflowScript: 2: Not a valid section definition: "agent". Some extra configuration is required. @ line 2, column 3.
agent
^
WorkflowScript: 1: Missing required section "agent" @ line 1, column 1.
pipeline
&
#125;
^
In this second example, the Jenkinsfile has been updated to include the missing any on agent. The linter now reports that the Pipeline is valid.
Jenkinsfile
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage ('Initialize') {
steps {
echo 'Placeholder.'
}
}
}
}
Linter output for valid Jenkinsfile
ssh -p 8675 localhost declarative-linter
<
./Jenkinsfile
Jenkinsfile successfully validated.
"Replay" Pipeline Runs with Modifications
Typically a Pipeline will be defined inside of the classic Jenkins web UI, or by committing to a Jenkinsfile in source control. Unfortunately, neither approach is ideal for rapid iteration, or prototyping, of a Pipeline. The "Replay" feature allows for quick modifications and execution of an existing Pipeline without changing the Pipeline configuration or creating a new commit.
Usage
To use the "Replay" feature:
Select a previously completed run in the build history.
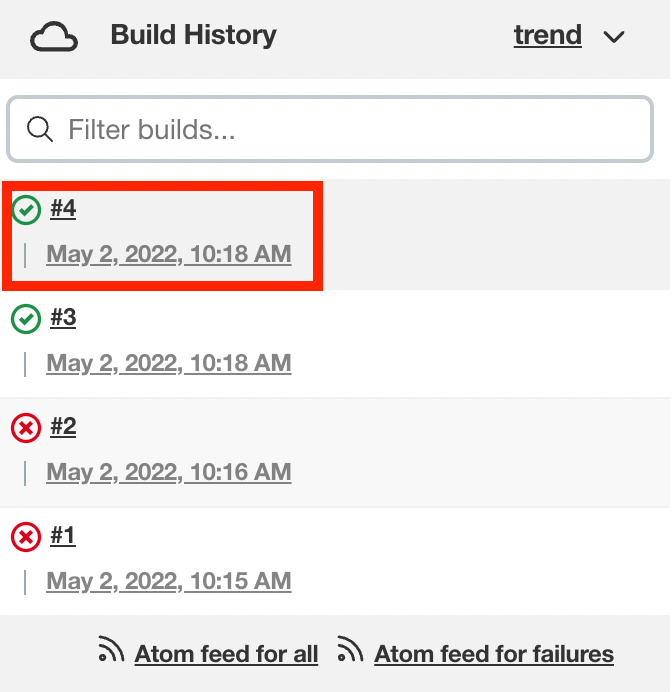
Click "Replay" in the left menu
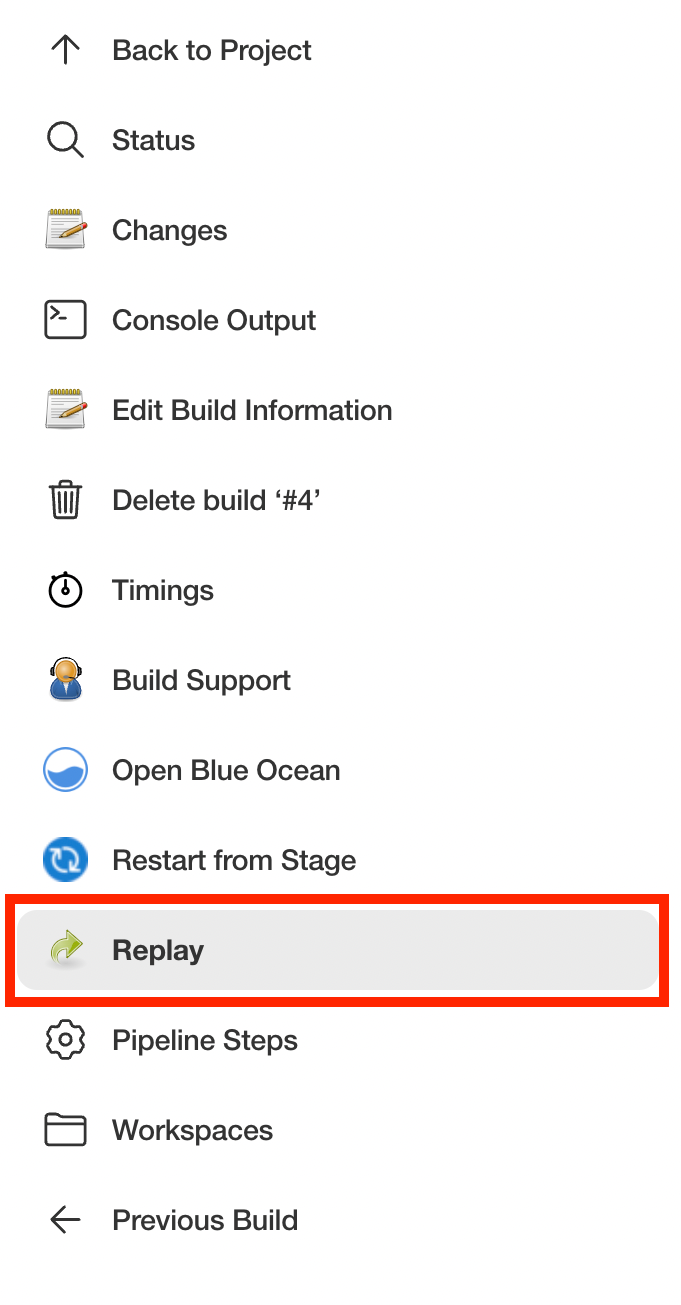
Make modifications and click "Run". In this example, we changed "ruby-2.3" to "ruby-2.4".
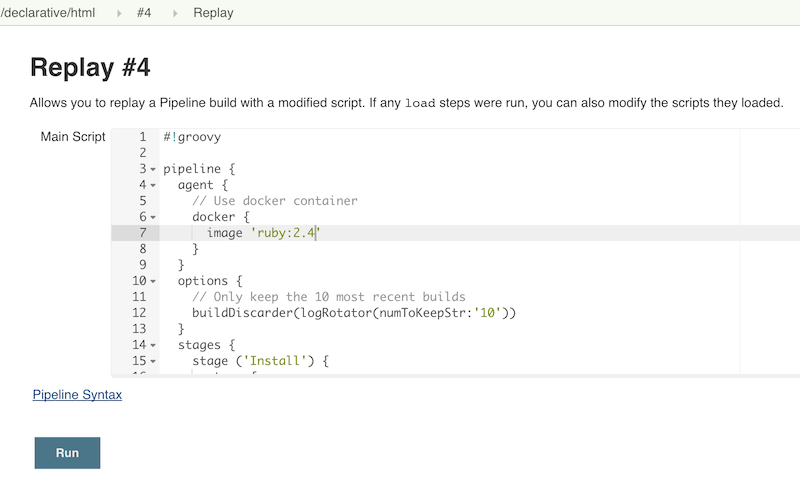
Check the results of changes
Once you are satisfied with the changes, you can use Replay to view them again, copy them back to your Pipeline job or Jenkinsfile, and then commit them using your usual engineering processes.
Features
Can be called multiple times on the same run - allows for easy parallel testing of different changes.
Can also be called on Pipeline runs that are still in-progress - As long as a Pipeline contained syntactically correct Groovy and was able to start, it can be Replayed.
Referenced Shared Library code is also modifiable - If a Pipeline run references a Shared Library, the code from the shared library will also be shown and modifiable as part of the Replay page.
Limitations
Pipeline runs with syntax errors cannot be replayed - meaning their code cannot be viewed and any changes made in them cannot be retrieved. When using Replay for more significant modifications, save your changes to a file or editor outside of Jenkins before running them. See JENKINS-37589
Replayed Pipeline behavior may differ from runs started by other methods - For Pipelines that are not part of a Multi-branch Pipeline, the commit information may differ for the original run and the Replayed run. See JENKINS-36453
Pipeline Unit Testing Framework
| The Pipeline Unit Testing Framework is a third-party tool that is not supported by the Jenkins Project. | |
|---|---|
The Pipeline Unit Testing Framework allows you to unit test Pipelines and Shared Libraries before running them in full. It provides a mock execution environment where real Pipeline steps are replaced with mock objects that you can use to check for expected behavior. New and rough around the edges, but promising. The README for that project contains examples and usage instructions.